10. 开始在Python中使用进程¶
在大多数操作系统中,每个程序在一个进程中运行。通常,我们通过双击一个应用程序的图标来启动程序。在本节中,我们简单地展示如何在Python中开启一个进程。进程有自己的地址空间,数据栈和其他的辅助数据来追踪执行过程;系统会管理所有进程的执行,通过调度程序来分配计算资源等。
10.2. 如何做…¶
执行第一个示例,我们需要敲入下面两个代码文件:
called_Process.pycalling_Process.py
你可以使用Python IDE(3.3.0)来编辑下面的文件:
called_Process 的代码如下:
print("Hello Python Parallel Cookbook!!")
closeInput = raw_input("Press ENTER to exit")
print"Closing calledProcess"
calling_Process 的代码如下:
## The following modules must be imported
import os
import sys
## this is the code to execute
program = "python"
print("Process calling")
arguments = ["called_Process.py"]
## we call the called_Process.py script
os.execvp(program, (program,) + tuple(arguments))
print("Good Bye!!")
运行例子的方法是,用Python IDE打开 calling_Process 程序然后按下F5.
在Python shell看到的输出如下:
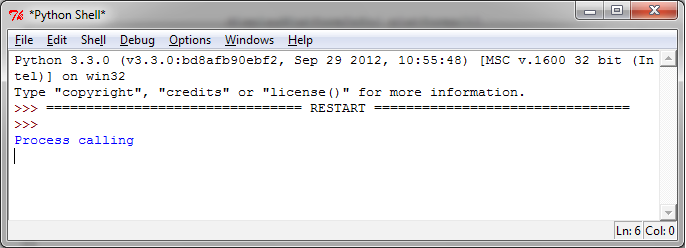
同时,系统的终端将看到如下输出:
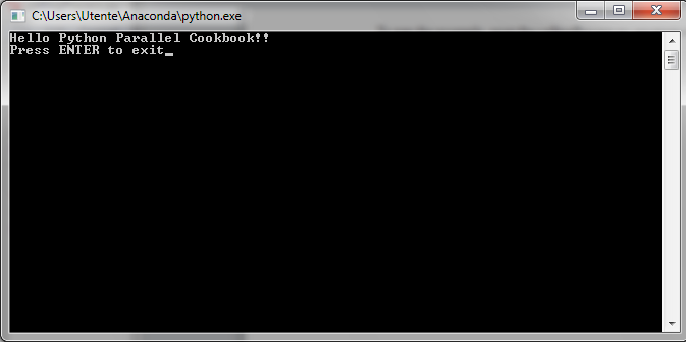
我们有两个进程运行,按下Enter可以关闭系统终端。
10.3. 如何做…¶
在前面的例子中, execvp 函数开启了一个新的进程,替换了当前的进程。注意”Good Bye”永远不会打印出来。相反,它会在当前的系统路径中搜索 called_Process ,将第二个参数的内容作为独立的变量传给程序,然后在当前环境上下文中执行。called_Process``中的 ``input() 仅仅用来管理当前系统的闭包。本节展示了基于进程的并行,我们在后面会介绍更多通过进程(multiprocessing模块)管理并行的方法。